1. Use Print Screen
This is the most common method to take screenshots. Pressing the “Print Screen” button will take the screenshot of the “Entire Visible Screen”.When we want to take a particular window, we can use “Alt+Print Screen”. Alt+PrintScreen will take only the particular window which is currently active.
2. Use gnome-screenshot
gnome-screenshot utility is part of the GNOME Desktop Environment, which can also be used to take screenshot. It also has a command line mode (gnome-screenshot)Launch the screenshot tool as shown below.
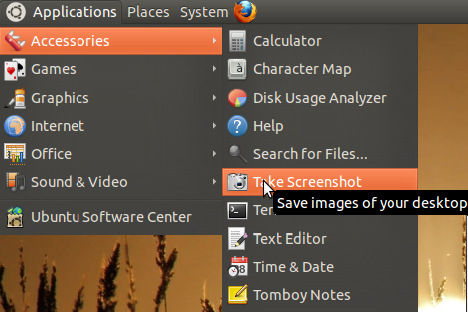
Capture the Entire Screen:
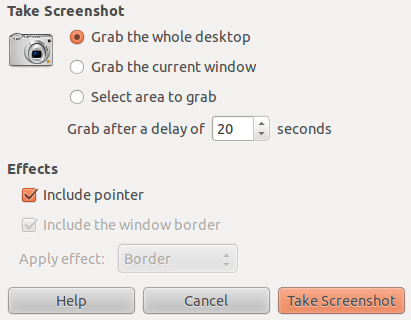
From the UI, to take a screenshot with entire screen, select “Grab the whole desktop” and click “Take Screenshot”.From the command-line, just type the command “gnome-screenshot” to do the same. The command will take a screenshot and provide a dialog to save it.
$ gnome-screenshot
Capture Only the Current Window:
From the UI, to take the screenshot of the current active window alone, select “Grab the Current Window” and click “Take Screenshot”.From the command-line, use the -w option as follows to do the same.
$ gnome-screenshot -w
Take Screenshot After Some Delay:
From the UI, you can also set a delay before taking the screenshots. Set the “Grab after a delay” to the required number of seconds. This will be really helpful when we need to take screen shots of navigation.From the command-line, use -d option to do the same. -d 2 is used for delaying the screenshot for 2 seconds. So within the 2 seconds, we can make the window which we want to take screenshot as active.
$ gnome-screenshot -w -d 2
Capture a Particular Area:
From the UI, if you want to take a particular rectangle area alone, then select “Grab a Particular area” and click “Take Screenshot”.From the command-line, use the -a option to do the same. Once this command is entered, the mouse pointer will be changed, and you can drag and select which area to take screenshot.
$ gnome-screenshot -a
Take Screenshot Including or Excluding Window Border:
From the UI, you can also include or exclude the window border by selecting/deselecting “Include the Window Border” option.From the command line, use -b/-B options respectively to do the same. This command will include the window border along with the screenshot.
$ gnome-screenshot -w -b
The following command will exclude the window border from the screenshot.$ gnome-screenshot -w -B
3. Use ImageMagic’s Import Command
ImageMagick is an open source software suite for displaying, converting, and editing raster image files. It comes with various command line tools, and one of that is “import”. Now we will see, how we can use import to take screenshots. You can install it by using apt-get on debian/ubuntu as follows:# apt-get install imagemagick
Capture Entire Screen using -window root option
Use the “-window root” option to take screenshot of the complete screen. The screenshot will be saved in the file name provided in the command line.$ import -window root Pictures/Image5.png
ImageMagick supports more that 100 file types. You can use any one of them to store the output.Capture a Particular Window/Area:
Type the following command, it will change the mouse pointer to “Cross” symbol. Select the window which you would like to take screenshot or click and drag to take screenshot of particular area.$ import calc.png
Include the frame using -frame option:
You can also include the “frame” of the window using the -frame option.$ import -frame Image6.png
Take Screenshot and Resize using -resize option:
You can also take screenshot and resize the screenshot using the -resize option. Pause option is used to make a delay before taking the screenshots.$ import -window root -resize 640 -pause 4 Pictures/Image7.png
Please refer “man import” for more number of options supported by import command.4. Use GIMP
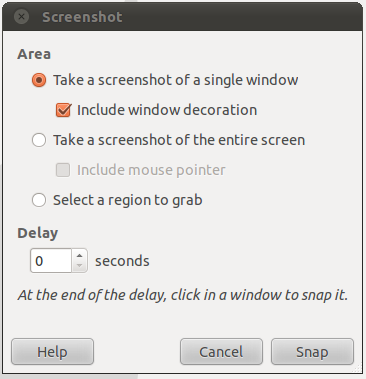
You can also take screenshot from gimp. Launch gimp, and click “File->Create->Screenshot”. A new dialog window will open with options similar to gnome-screenshot.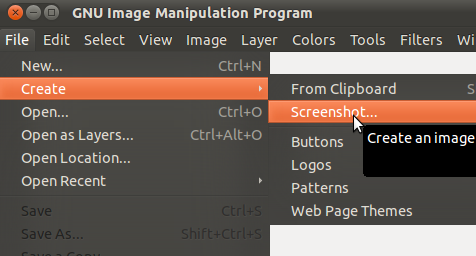
Source : http://www.thegeekstuff.com
No comments:
Post a Comment